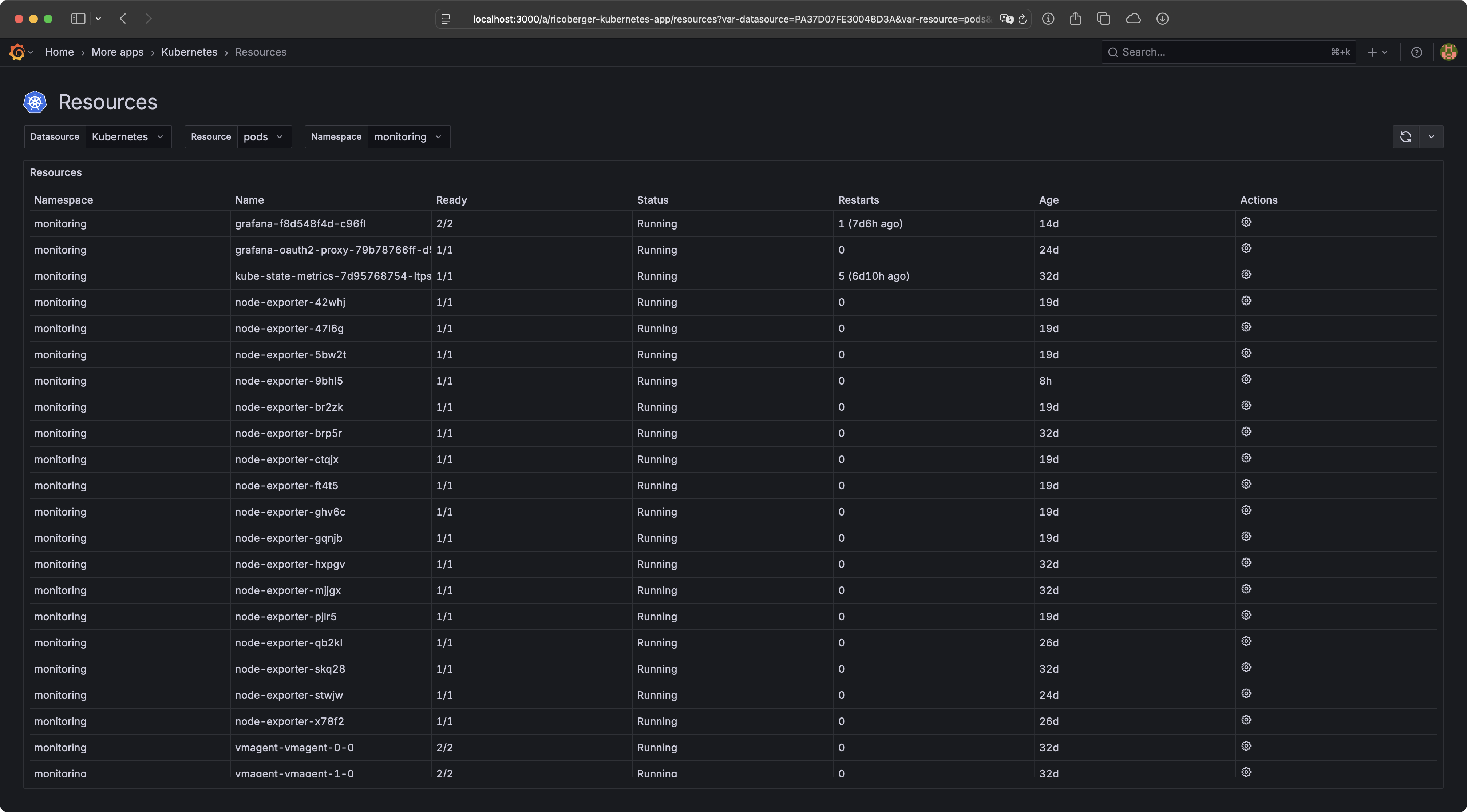
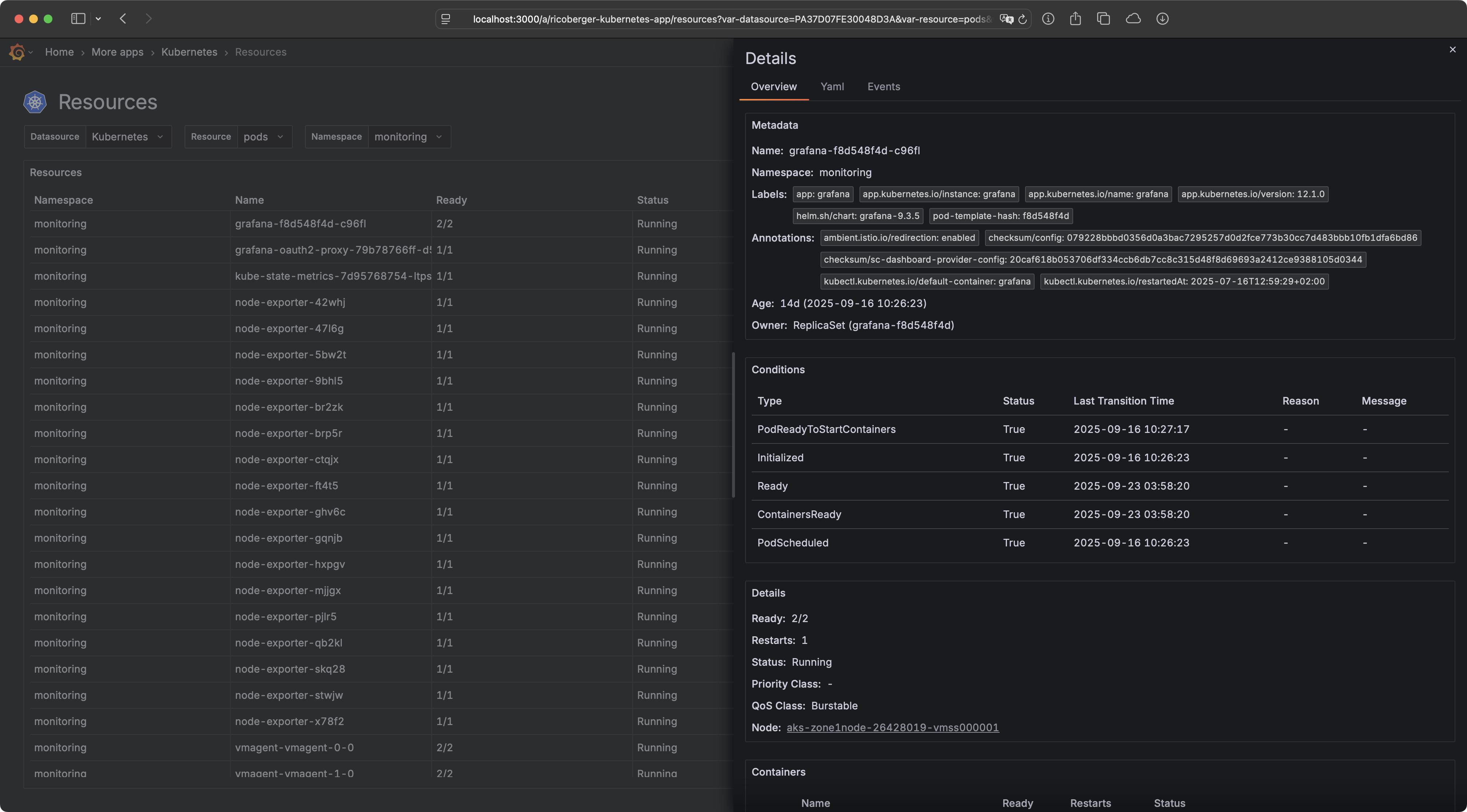
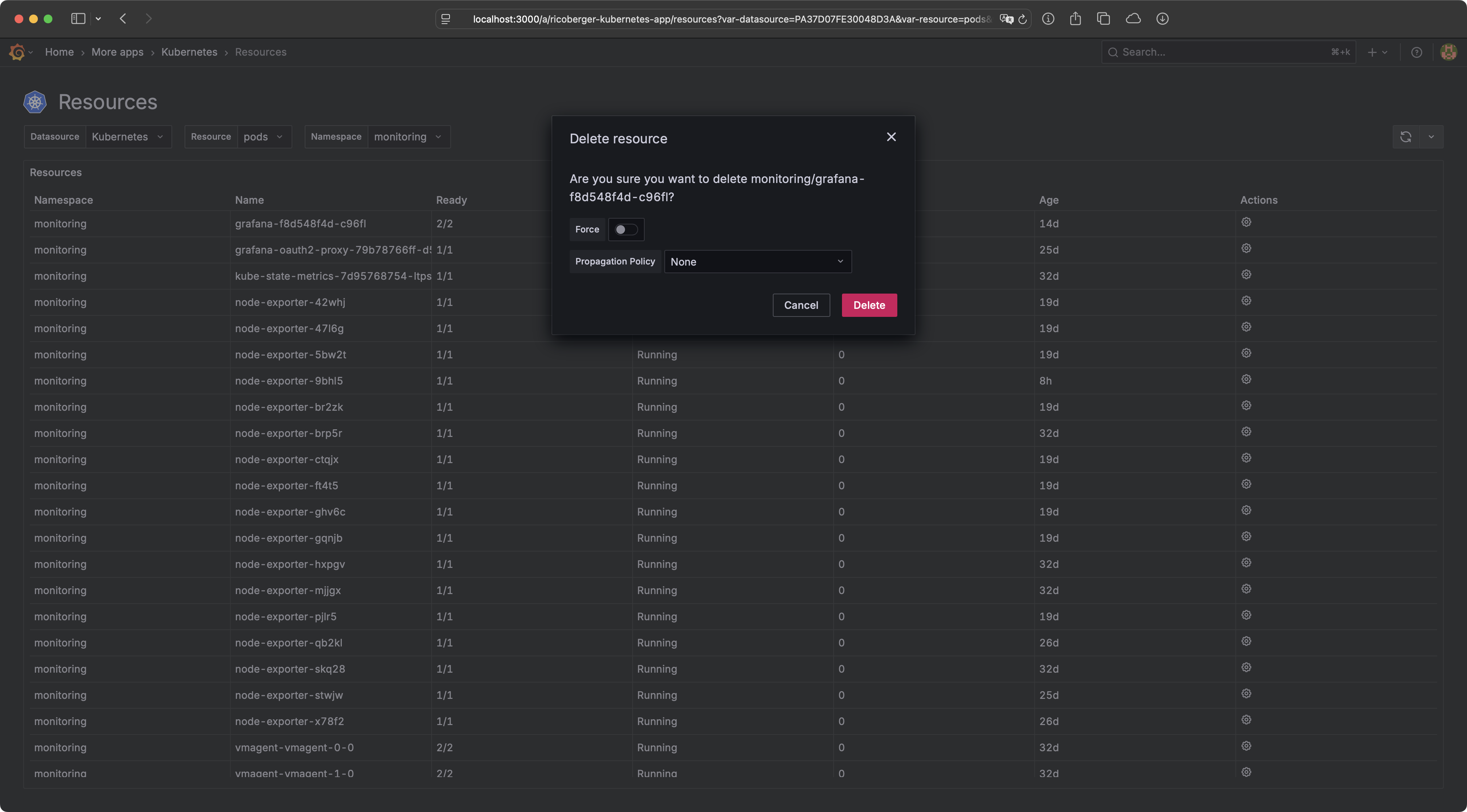
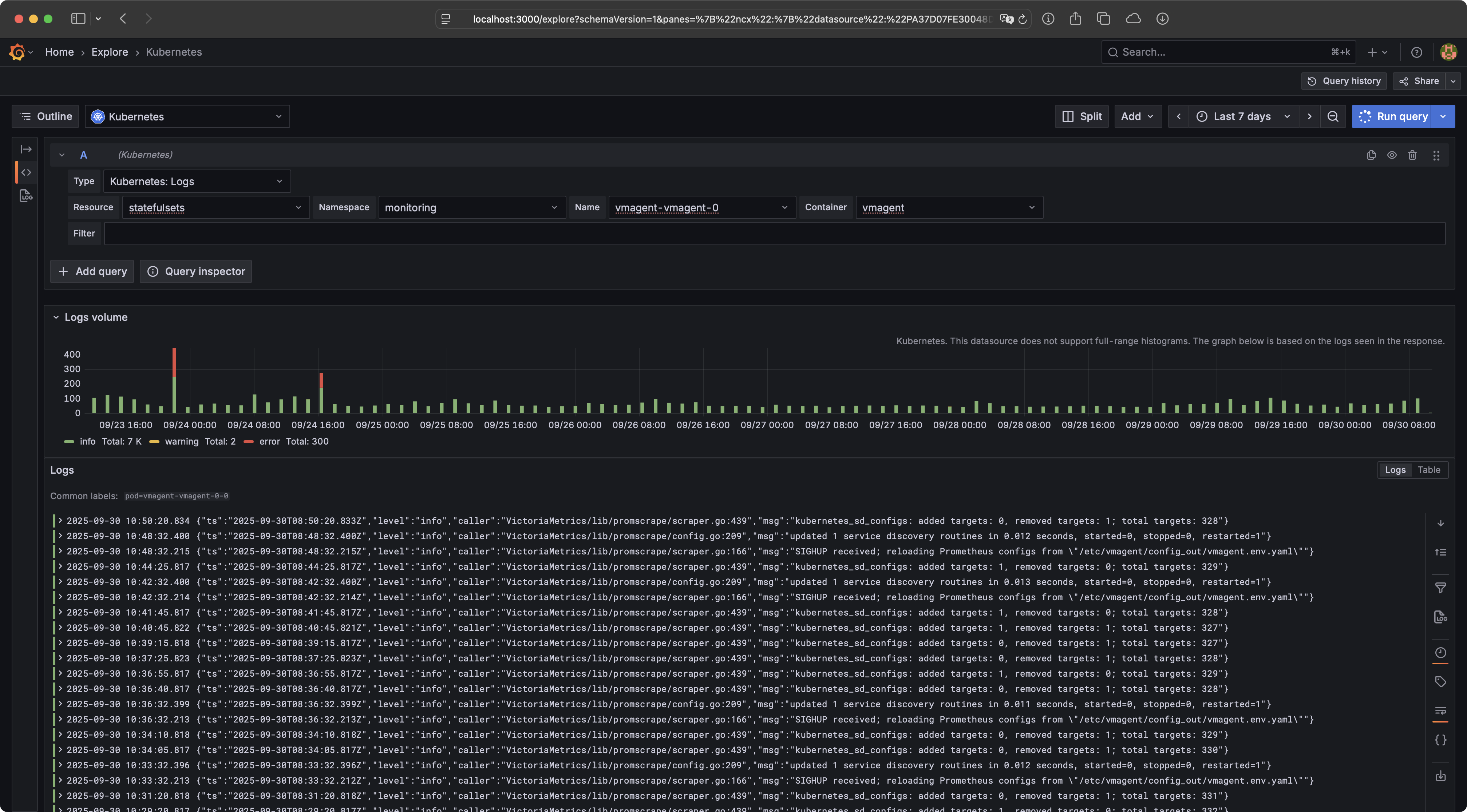
The Grafana Kubernetes Plugin allows you to explore your Kubernetes resources and logs directly within Grafana. The plugin also provides several actions to interact with your resources, including editing, deleting, and scaling them. Last but not least, the plugin also supports other cloud native tools such as Helm and Flux.
- View Kubernetes resources like Pods, DaemonSets, Deployments, StatefulSets, etc.
- Includes support for Custom Resource Definitions.
- Filter and search for resources, by Namespace, label selectors and field selectors.
- Get a fast overview of the status of resources, including detailed information and events.
- Modify resources, by adjusting the YAML manifest files or using the built-in actions for scaling, restarting, creating or deleting resources.
- View logs of Pods, DaemonSets, Deployments, StatefulSets and Jobs.
- Automatic JSON parsing of log lines and filtering of logs by time range and regular expressions.
- Role-based access control (RBAC), based on Grafana users and teams, to authorize all Kubernetes requests.
- Generate Kubeconfig files, so users can access the Kubernetes API using tools
like
kubectlfor exec and port-forward actions. - Analyse and debug Kubernetes workloads using the Grafana LLM plugin.
- Integrations for metrics and traces:
- Metrics: View metrics for Kubernetes resources like Pods, Nodes, Deployments, etc. using a Prometheus datasource.
- Traces: Link traces from Pod logs to a tracing datasource like Jaeger.
- Integrations for other cloud-native tools like Helm and Flux:
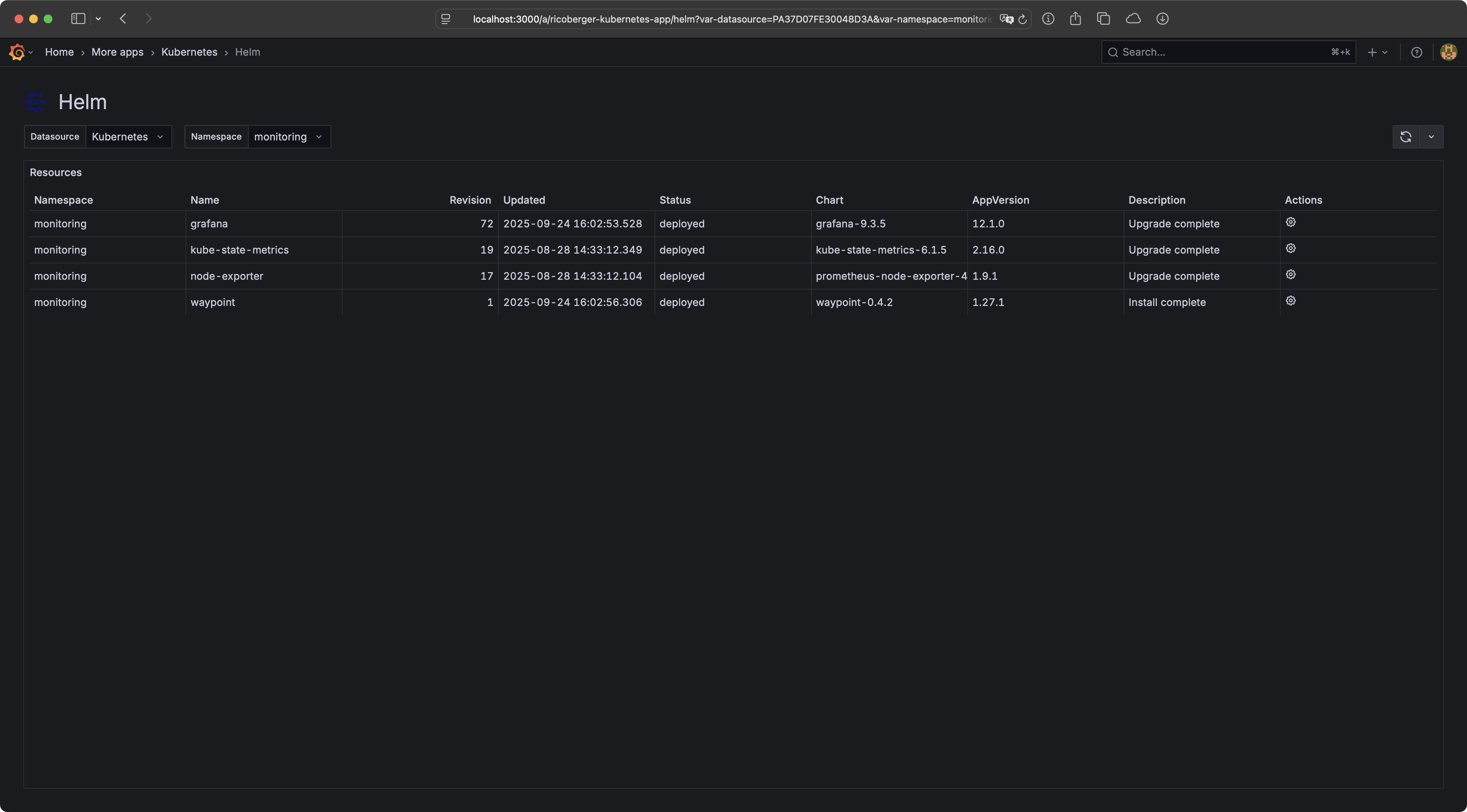
- Helm: View Helm releases including the history, rollback and uninstall Helm releases.
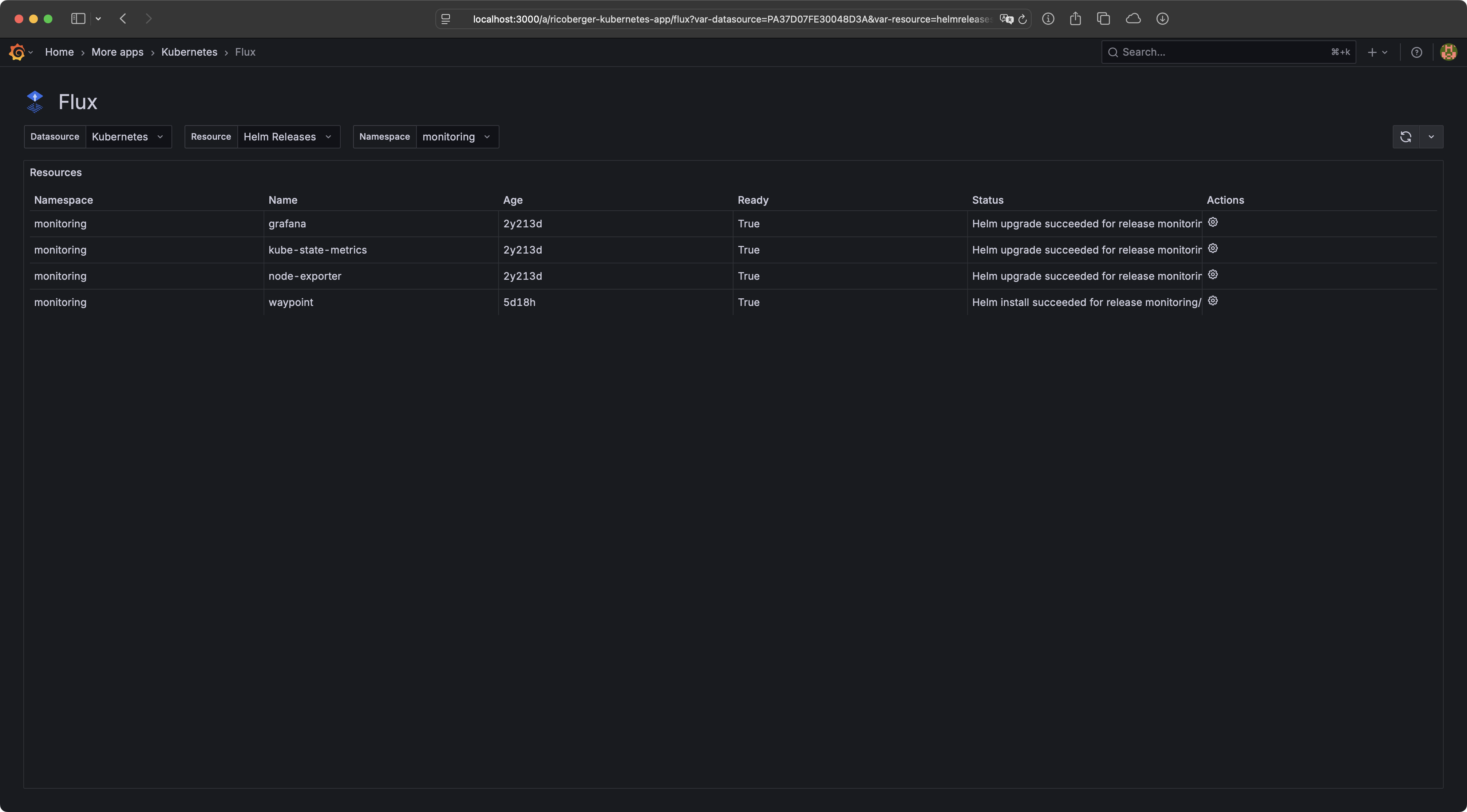
- Flux: View Flux resources, reconcile, suspend and resume Flux resources.
- Before you can install the plugin, you have to add
ricoberger-kubernetes-appandricoberger-kubernetes-datasourceto theallow_loading_unsigned_pluginsconfiguration option or to theGF_PLUGINS_ALLOW_LOADING_UNSIGNED_PLUGINSenvironment variable. - The plugin can then be installed by adding
ricoberger-kubernetes-app@<VERSION>@https://github.com/ricoberger/grafana-kubernetes-plugin/releases/download/v<VERSION>/ricoberger-kubernetes-app-<VERSION>.zipto thepreinstall_syncconfiguration option or theGF_PLUGINS_PREINSTALL_SYNCenvironment variable. - Once the plugin is installed, you have to activate the app in you Grafana
instance by navigating to Administration -> Plugins and data ->
Plugins -> Kubernetes and clicking on the Enable button
(
<GRAFANA-INSTANCE-URL>/plugins/ricoberger-kubernetes-app). - Last but not least, you have to add a new Kubernetes data source to your Grafana instance.
[plugins]
allow_loading_unsigned_plugins = ricoberger-kubernetes-app,ricoberger-kubernetes-datasource
preinstall_sync = ricoberger-kubernetes-app@0.2.0@https://github.com/ricoberger/grafana-kubernetes-plugin/releases/download/v0.2.0/ricoberger-kubernetes-app-0.2.0.zipexport GF_PLUGINS_ALLOW_LOADING_UNSIGNED_PLUGINS=ricoberger-kubernetes-app,ricoberger-kubernetes-datasource
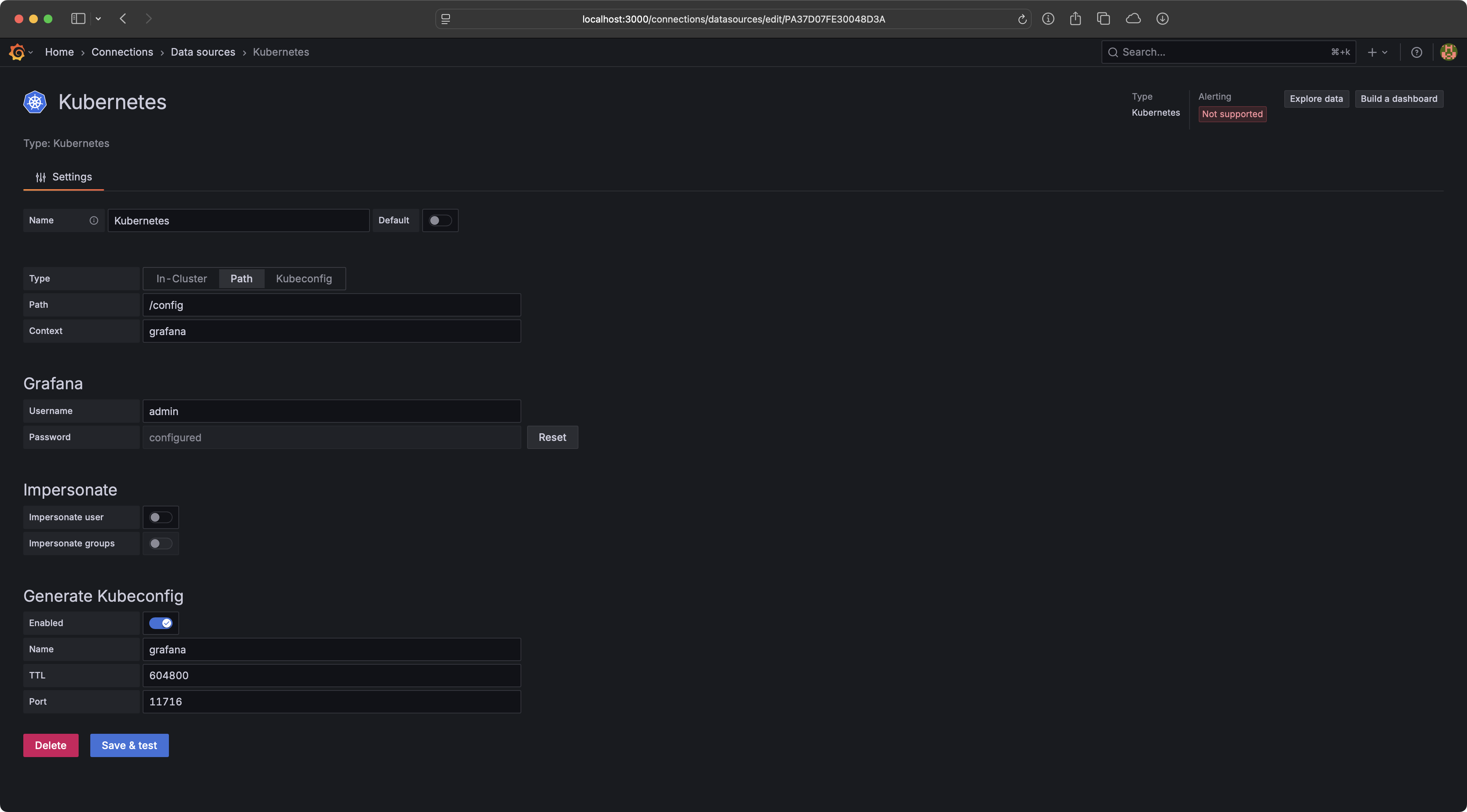
export GF_PLUGINS_PREINSTALL_SYNC=ricoberger-kubernetes-app@0.2.0@https://github.com/ricoberger/grafana-kubernetes-plugin/releases/download/v0.2.0/ricoberger-kubernetes-app-0.2.0.zipTo add a new Kubernetes cluster to Grafana, create a new Kubernetes data source.
You can choose between multiple providers to add a Kubernetes cluster:
- In-Cluster: Use a ServiceAccount mounted to your Grafana Pods, to authenticate against the Kubernetes cluster.
- Path: Provide the path to a Kubeconfig file and the context, which should be used from this file.
- Kubeconfig: Upload a Kubeconfig file and store it within Grafana. The Kubeconfig file can only contain one context.
To use the Impersonate and Generate Kubeconfig features of the plugin,
you have to enable basic authentication first, e.g. by setting the
GF_AUTH_BASIC_ENABLED environment variable to true or by enabling basic auth
in the
Grafana configuration.
Afterwards you have to provide a Grafana username and password for the plugin,
so that the plugin can interact with the Grafana API. The provided user should
have the Admin role.
The plugin can impersonate a Grafana user and the groups of the user when making requests against the Kubernetes API. This means that you can use role-based access control (RBAC) within the plugin.
If you have a user with the login admin you can create the following
ClusterRole and ClusterRoleBinding to allow this user to only list and get Pods
within the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl create clusterrole grafana-admin-user --verb list,get --resource pods
kubectl create clusterrolebinding grafana-admin-user --clusterrole grafana-admin-user --user adminIf you have a team called admin you can create the following ClusterRole and
ClusterRoleBinding to allow all members of this team to only list and get Pods
within the Kubernetes cluster:
kubectl create clusterrole grafana-admin-team --verb list,get --resource pods
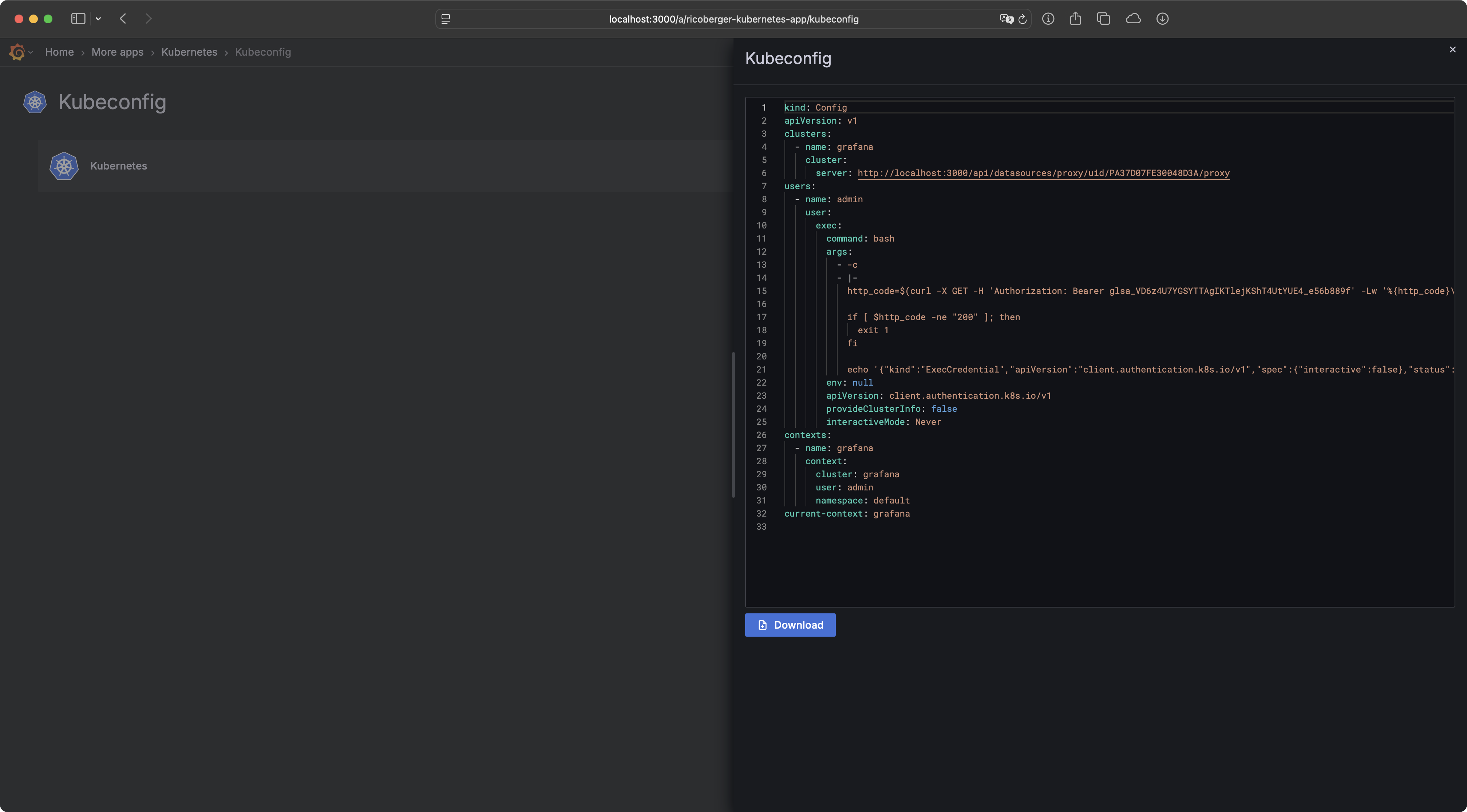
kubectl create clusterrolebinding grafana-admin-team --clusterrole grafana-admin-team --group adminThe Grafana Kubernetes Plugin can also be used to generate a Kubeconfig for your
users, so that they can use kubectl for exec and port-forward actions, which
are not directly supported by the plugin.
If enabled the plugin will create a personal Grafana service account and service account token for all users. This token is then used in the Kubeconfig, so that the user gets access to Grafana, which will then forward the request to the Kubernetes API. This feature also uses the Impersonate feature if enabled.
To use this feature you have to provide a name for the Kubeconfig file which is generated, a time-to-live for the genated service account token in seconds and a port, which will be used to start the server responsible for authenticating the user and proxing the request to the Kubernetes API.
To make it easier to download the generated Kubeconfig file, the
kubectl-grafana kubectl plugin can be used. The plugin can be downloaded from
the
releases page
or by running the following command:
go install github.com/ricoberger/grafana-kubernetes-plugin/cmd/kubectl-grafana@latestWhen the kubectl plugin is installed, the following command can be used to download the generated Kubeconfig. If the provided Kubeconfig file already contains a Kubeconfig it will be merged, with the downloaded Kubeconfig having a higher priority.
kubectl grafana kubeconfig --grafana-url <GRAFANA-INSTANCE-URL> --grafana-datasource <DATASOURCE-UID> --kubeconfig <PATH-TO-KUBECONFIG-FILE>Integrations allow you to integrate the Kubernetes datasource with other datasources to view metrics or traces related to your Kubernetes resources.
To view the metrics of your Kubernetes resources you have to provide the UID of a Prometheus datasource and the job label for the kubelet, kube-state-metrics and node-exporter metrics.
To view the traces of your Kubernetes logs you have to provide a query for your
traces. In the query you can use the ${__value.raw} variable which will be
replaced with the actual trace id. For example, the following query can be used
to link to a Jaeger datasource:
{"datasource":"jaeger","queries":[{"query":"${__value.raw}","refId":"A"}]}.
If you want to contribute to the project, please read through the contribution guideline. Please also follow our code of conduct in all your interactions with the project.