-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 6
Home
Up to now, the research work on machine learning on graph-shaped data is sparse In this survey, we investigate the state of the art of the intersection in machine learning techniques and database systems with a focus on graph databases (i.e. graph-databases for machine learning). We classify the found techniques into those that are supplied with the data of database systems (external) or those that create a symbiosis with the database systems (internal). A crucial investigation is to determine time-consuming steps in machine learning algorithms and to identify the optimization potential of employing suitable data management techniques (e.g., suitable graph operators) for their performance improvement.
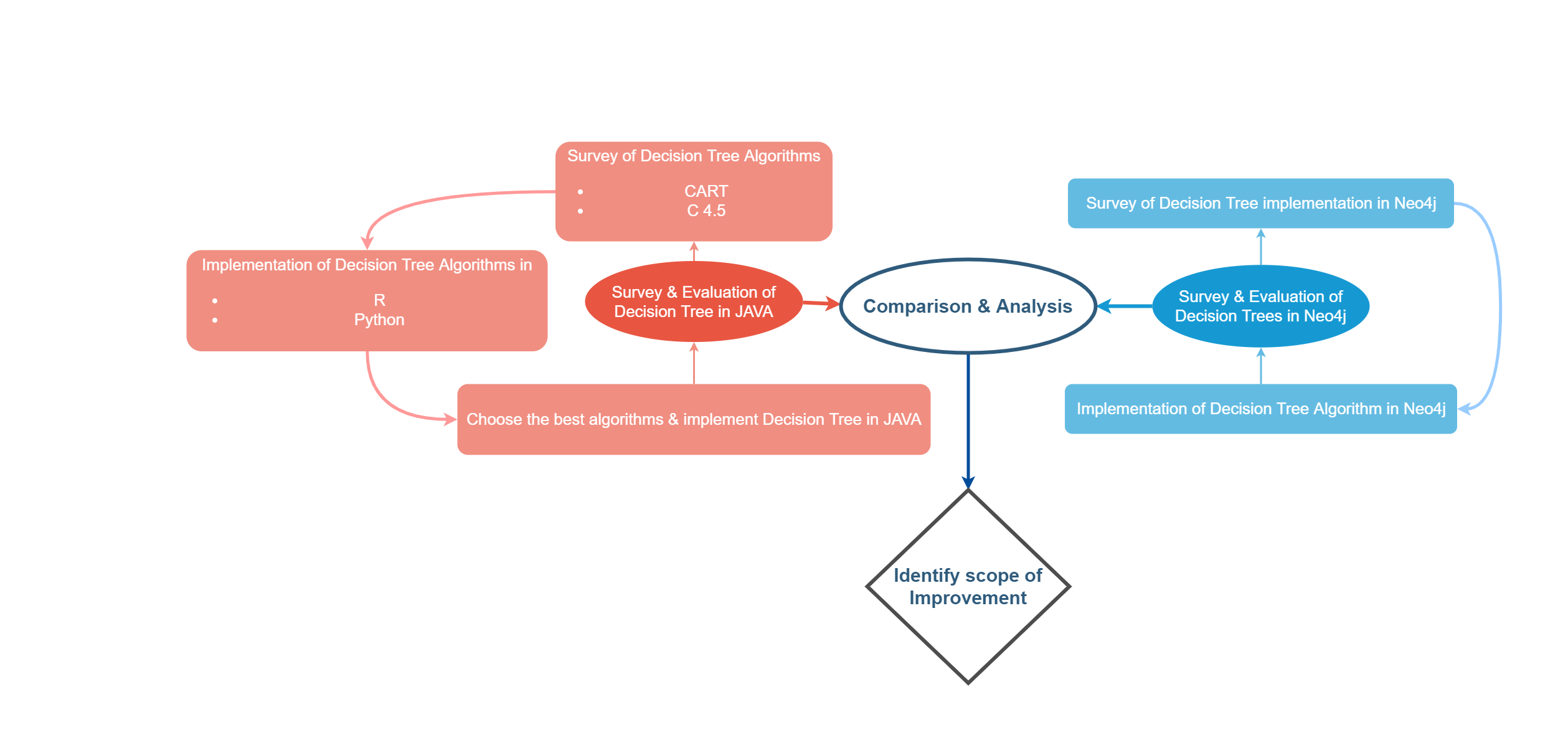
We investigate how to provision graph-shaped data for machine learning in a suitable and performant way. The idea is that instead of translating the graph data into CSV files and feeding the files into a machine learning algorithm, the already populated graph showing all attribute combinations as edges is a far more discrete input for a machine learning algorithm. For example, the graph-shaped data already represents a tree structure that could be traversed by decision tree learning, requiring only suitable graph operators and minor adaptation of the machine learning algorithms. Similar to decision tree learning, we assume that other machine learning algorithms can benefit from graph-shaped data. As a result, we expect to identify a set of graph operators that allow for efficient data provisioning for different external machine learning algorithms leading to a significant performance boost of the machine learning performance.
In the previous work package, we investigated how to feed external machine learning algorithms with data from the graph. The next step is a deeper integration of those algorithms into the graph database. Promising integration aspects are specialized indexes, extensions of the query language, and additional properties of nodes and edges that support machine learning algorithms or represent intermediate learning results. Another idea is the addition of nodes into the graph, which represent the machine learning algorithm. For instance, a graph neural network could be directly derived from the stored graph data by adding edges with neural networks and nodes with recurrent units. As a consequence, these interconnected neural networks and recurrent units could also be stored with their data representation. As a result, we expect not only faster predictions but also an increased explain-ability of the resulting predictions of the neural network, because the classifier is directly calculated on the data graph, and the connection between data and classifier becomes more apparent. The result of this work package is a set of integration concepts that allow to efficiently integrate machine learning algorithms into graph databases. This also includes necessary adaptations that need to be done on the storage structures, index structures, and operators from the previous work packages in order to provide peak performance.