-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 5
Migrate to RESTful Automation API
From ArcGIS Earth 1.11, ArcGIS Earth Automation API has been updated from .NET WCF NamedPipe to ASP.NET Core, which creates a .NET Core Generic Host to implement a RESTful Automation API.
With the ASP.NET Core by .NET Generic Host, ArcGIS Earth Automation API introduces a new RESTful API and includes enriched capabilities:
- Added support for more data types.
- Added an interface to clear workspace.
- Updated camera class with position and removed mapPoint.
- Updated camera class with tilt parameter and removed pitch parameter.
- Updated the response information of adding a layer by id, data loaded status returned.
- Supported configure Automation API by users.
- Added a ready-to-use sample page.
- Added a web API help page with Swagger / OpenAPI.
Please check the release notes of ArcGIS Earth Automation API for more information.
Now, please forget the complicated and cumbersome code of NamedPipe. In the new RESTful code, you only need the following simple code to achieve the previously desired functions.
Get Camera
private async Task<string> GetCamera()
{
// API url
string cameraRequestUrl = "http://localhost:8000/arcgisearth/Camera";
// Send request and get response
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await httpClient.GetAsync(cameraRequestUrl);
// Get string content form the response
HttpContent content = responseMessage.Content;
return await content.ReadAsStringAsync();
}Set Camera
private async Task<string> SetCamera(string inputJsonStr)
{
// API url
string cameraRequestUrl = "http://localhost:8000/arcgisearth/Camera";
// Convert string request content to HttpContent
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(inputJsonStr);
var byteArrayContent = new ByteArrayContent(data);
byteArrayContent.Headers.Add("Content-Type", "application/json");
// Send request and get response
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await httpClient.PutAsync(cameraRequestUrl, byteArrayContent);
// Get string content form the response
HttpContent content = responseMessage.Content;
return await content.ReadAsStringAsync();
}Add Layer
private async Task<string> AddLayer(string inputJsonStr)
{
// API url
string layerRequestUrl = "http://localhost:8000/arcgisearth/Layer";
// Convert string request content to HttpContent
byte[] data = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(inputJsonStr);
var byteArrayContent = new ByteArrayContent(data);
byteArrayContent.Headers.Add("Content-Type", "application/json");
// Send request and get response
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = await httpClient.PostAsync(layerRequestUrl, byteArrayContent);
return await GetResponseContent(responseMessage);
}For more use cases, you can refer to the AutomationAPIHelper class in the ArcGISEarth.AutoAPI.Utils project. This class encapsulates all the methods that can be used.
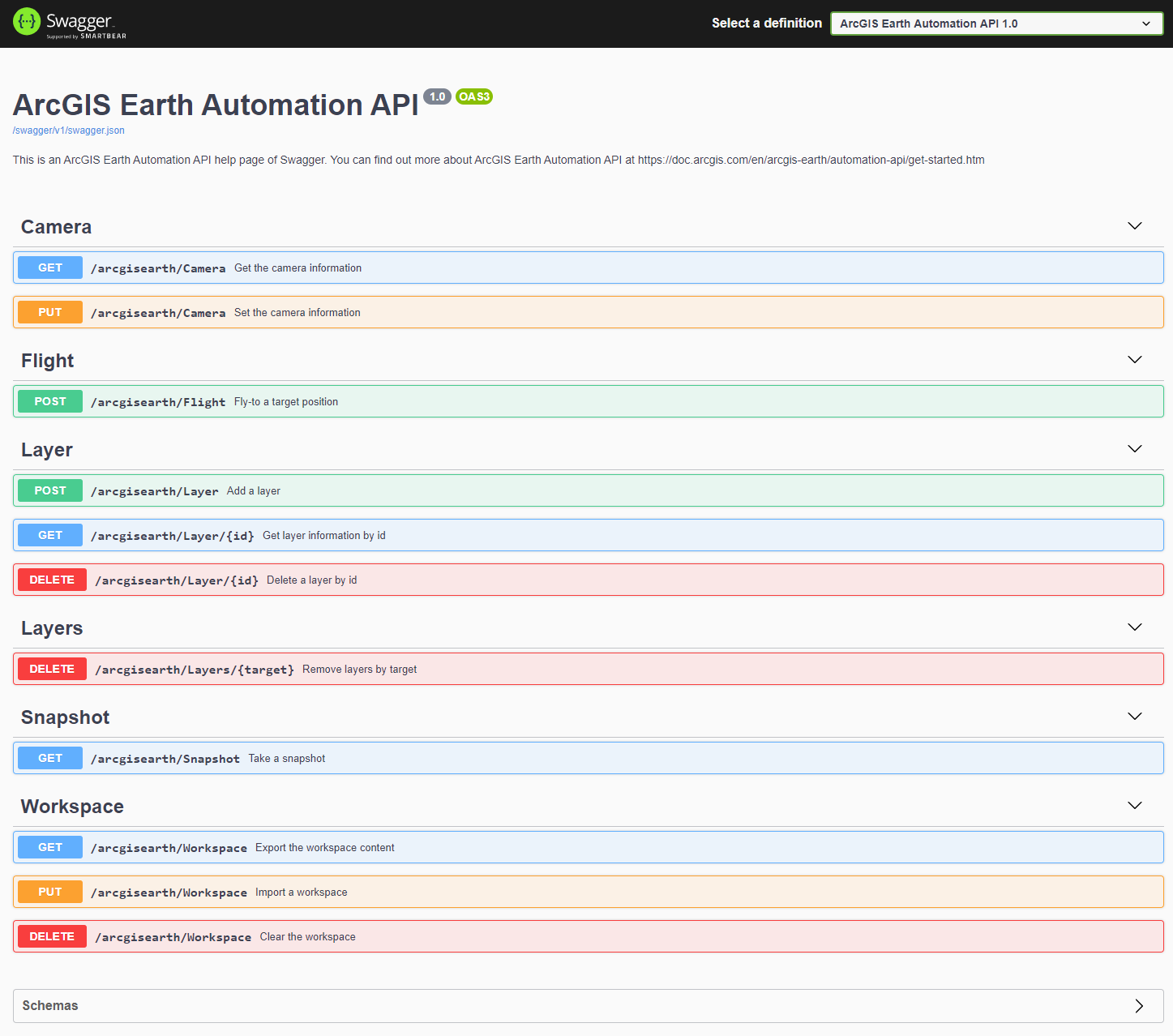
ArcGIS Earth Automation API uses Swashbuckle.AspNetCore, an open source project, to generate Swagger documents and implement Swagger UI to offer a web-based UI that provides information.
Once the ArcGIS Earth Automation API is enabled, you can find the Swagger link from the Advanced application settings. The default url is http://localhost:8000/swagger/index.html
The Swagger UI looks like below: