diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md
index 41436eb78..ad83c82ad 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0073_set_matrix_zeroes/readme.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
Medium
-Given an `m x n` integer matrix `matrix`, if an element is `0`, set its entire row and column to `0`'s, and return _the matrix_.
+Given an `m x n` integer matrix `matrix`, if an element is `0`, set its entire row and column to `0`'s.
You must do it [in place](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm).
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md
index ffe4e741a..896f23130 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0074_search_a_2d_matrix/readme.md
@@ -2,11 +2,15 @@
Medium
-Write an efficient algorithm that searches for a value in an `m x n` matrix. This matrix has the following properties:
+You are given an `m x n` integer matrix `matrix` with the following two properties:
-* Integers in each row are sorted from left to right.
+* Each row is sorted in non-decreasing order.
* The first integer of each row is greater than the last integer of the previous row.
+Given an integer `target`, return `true` _if_ `target` _is in_ `matrix` _or_ `false` _otherwise_.
+
+You must write a solution in `O(log(m * n))` time complexity.
+
**Example 1:**

diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md
index f3ea592c4..f64e105ca 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0075_sort_colors/readme.md
@@ -20,23 +20,11 @@ You must solve this problem without using the library's sort function.
**Output:** [0,1,2]
-**Example 3:**
-
-**Input:** nums = [0]
-
-**Output:** [0]
-
-**Example 4:**
-
-**Input:** nums = [1]
-
-**Output:** [1]
-
**Constraints:**
* `n == nums.length`
* `1 <= n <= 300`
-* `nums[i]` is `0`, `1`, or `2`.
+* `nums[i]` is either `0`, `1`, or `2`.
**Follow up:** Could you come up with a one-pass algorithm using only constant extra space?
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md
index 75d66f898..cbe4b8e9a 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0076_minimum_window_substring/readme.md
@@ -2,12 +2,10 @@
Hard
-Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return _the **minimum window substring** of_ `s` _such that every character in_ `t` _(**including duplicates**) is included in the window. If there is no such substring__, return the empty string_ `""`_._
+Given two strings `s` and `t` of lengths `m` and `n` respectively, return _the **minimum window**_ **substring** _of_ `s` _such that every character in_ `t` _(**including duplicates**) is included in the window_. If there is no such substring, return _the empty string_ `""`.
The testcases will be generated such that the answer is **unique**.
-A **substring** is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
-
**Example 1:**
**Input:** s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0077_combinations/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0077_combinations/readme.md
index eaae4b479..2266cb505 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0077_combinations/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0077_combinations/readme.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
Medium
-Given two integers `n` and `k`, return _all possible combinations of_ `k` _numbers out of the range_ `[1, n]`.
+Given two integers `n` and `k`, return _all possible combinations of_ `k` _numbers chosen from the range_ `[1, n]`.
You may return the answer in **any order**.
@@ -10,13 +10,17 @@ You may return the answer in **any order**.
**Input:** n = 4, k = 2
-**Output:** [ [2,4], [3,4], [2,3], [1,2], [1,3], [1,4], ]
+**Output:** [[1,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,3],[2,4],[3,4]]
+
+**Explanation:** There are 4 choose 2 = 6 total combinations. Note that combinations are unordered, i.e., [1,2] and [2,1] are considered to be the same combination.
**Example 2:**
**Input:** n = 1, k = 1
-**Output:** [[1]]
+**Output:** [[1]]
+
+**Explanation:** There is 1 choose 1 = 1 total combination.
**Constraints:**
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md
index 9719983bd..788b97254 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0078_subsets/readme.md
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
Medium
-Given an integer array `nums` of **unique** elements, return _all possible subsets (the power set)_.
+Given an integer array `nums` of **unique** elements, return _all possible_ **subset** _(the power set)_.
The solution set **must not** contain duplicate subsets. Return the solution in **any order**.
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0080_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array_ii/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0080_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array_ii/readme.md
index fa021a5f9..4ed899fe3 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0080_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array_ii/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0080_remove_duplicates_from_sorted_array_ii/readme.md
@@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ The judge will test your solution with the following code:
int[] expectedNums = [...]; // The expected answer with correct length
int k = removeDuplicates(nums); // Calls your implementation
-
+
assert k == expectedNums.length;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
assert nums[i] == expectedNums[i];
@@ -46,4 +46,4 @@ If all assertions pass, then your solution will be **accepted**.
* 1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104
* -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
-* `nums` is sorted in **non-decreasing** order.
\ No newline at end of file
+* `nums` is sorted in **non-decreasing** order.
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0088_merge_sorted_array/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0088_merge_sorted_array/readme.md
index c75ddb8c5..5e6d26581 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0088_merge_sorted_array/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0088_merge_sorted_array/readme.md
@@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ The final sorted array should not be returned by the function, but instead be _s
**Output:** [1,2,2,3,5,6]
-**Explanation:** The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6]. The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
+**Explanation:** The arrays we are merging are [1,2,3] and [2,5,6]. The result of the merge is [1,2,2,3,5,6] with the underlined elements coming from nums1.
**Example 2:**
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md
index 99fb9f158..87e8d704a 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0094_binary_tree_inorder_traversal/readme.md
@@ -6,39 +6,35 @@ Given the `root` of a binary tree, return _the inorder traversal of its nodes' v
**Example 1:**
-
-
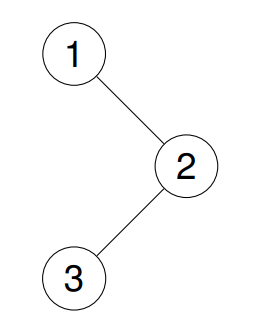
**Input:** root = [1,null,2,3]
-**Output:** [1,3,2]
-
-**Example 2:**
+**Output:** [1,3,2]
-**Input:** root = []
+**Explanation:**
-**Output:** []
+
-**Example 3:**
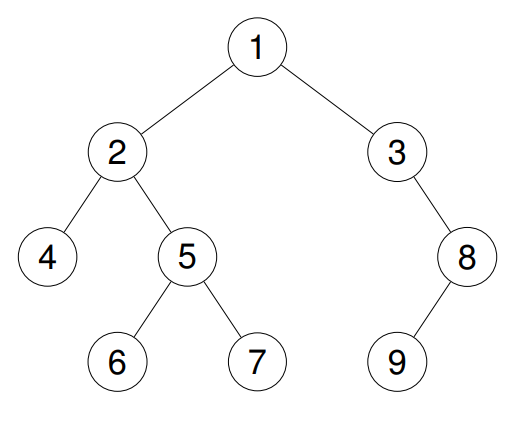
+**Example 2:**
-**Input:** root = [1]
+**Input:** root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,8,null,null,6,7,9]
-**Output:** [1]
+**Output:** [4,2,6,5,7,1,3,9,8]
-**Example 4:**
+**Explanation:**
-
+
-**Input:** root = [1,2]
+**Example 3:**
-**Output:** [2,1]
+**Input:** root = []
-**Example 5:**
+**Output:** []
-
+**Example 4:**
-**Input:** root = [1,null,2]
+**Input:** root = [1]
-**Output:** [1,2]
+**Output:** [1]
**Constraints:**
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0097_interleaving_string/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0097_interleaving_string/readme.md
index 613d1d5ed..66eac61ec 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0097_interleaving_string/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0097_interleaving_string/readme.md
@@ -4,7 +4,7 @@ Medium
Given strings `s1`, `s2`, and `s3`, find whether `s3` is formed by an **interleaving** of `s1` and `s2`.
-An **interleaving** of two strings `s` and `t` is a configuration where they are divided into **non-empty** substrings such that:
+An **interleaving** of two strings `s` and `t` is a configuration where `s` and `t` are divided into `n` and `m` **substring** respectively, such that:
* s = s1 + s2 + ... + sn
* t = t1 + t2 + ... + tm
@@ -19,13 +19,17 @@ An **interleaving** of two strings `s` and `t` is a configuration where they are
**Input:** s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbcbcac"
-**Output:** true
+**Output:** true
+
+**Explanation:** One way to obtain s3 is: Split s1 into s1 = "aa" + "bc" + "c", and s2 into s2 = "dbbc" + "a". Interleaving the two splits, we get "aa" + "dbbc" + "bc" + "a" + "c" = "aadbbcbcac". Since s3 can be obtained by interleaving s1 and s2, we return true.
**Example 2:**
**Input:** s1 = "aabcc", s2 = "dbbca", s3 = "aadbbbaccc"
-**Output:** false
+**Output:** false
+
+**Explanation:** Notice how it is impossible to interleave s2 with any other string to obtain s3.
**Example 3:**
diff --git a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md
index 7faf88cd5..3ca83ba09 100644
--- a/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md
+++ b/src/main/java/g0001_0100/s0098_validate_binary_search_tree/readme.md
@@ -6,8 +6,8 @@ Given the `root` of a binary tree, _determine if it is a valid binary search tre
A **valid BST** is defined as follows:
-* The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **less than** the node's key.
-* The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **greater than** the node's key.
+* The left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **strictly less than** the node's key.
+* The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys **strictly greater than** the node's key.
* Both the left and right subtrees must also be binary search trees.
**Example 1:**