-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 88
Binary Logical Graph Operators
This section provides an overview of binary graph operators, which consume two graphs as input.
| Binary Logical Graph Operators |
|---|
| Combination |
| Overlap |
| Exclusion |
| Equality |
| VertexFusion |
Given two graphs, the combine operator creates a LogicalGraph that includes the edges and vertices of both graphs.
It is implemented by the combine() function of the LogicalGraph. The combine function takes a LogicalGraph as its input and outputs a new
LogicalGraph that includes the elements of both graphs.
Consider the social graph from our quickstart section.
We use the combine function to retrieve all Person older than 30 of both graphs.
// Combine both graphs
LogicalGraph combination = n1.combine(n2)
// Retrieve the persons that are older than 30
.subgraph(
v -> v.getLabel().equals("Person") && v.getPropertyValue("age").getInt() >= 30,
e -> false
);The resulting graph looks as follows:

Given two graphs, the overlap operator extracts their common vertices and edges resulting in a new LogicalGraph.
It is implemented by the overlap() function of the LogicalGraph. The overlap function takes a LogicalGraph as its input and outputs a new
LogicalGraph consisting of the common elements in both graphs.
Consider the social graph from our quickstart section.
We use the overlap function to retrieve the common elements in both graphs.
LogicalGraph overlap = n2.overlap(n1);The resulting graph looks as follows:
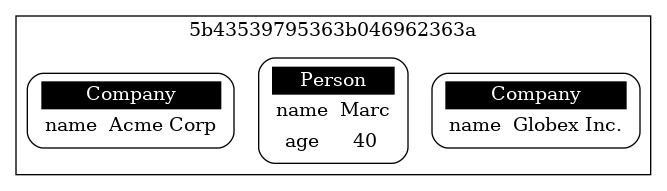
The overlap graph contains all the common elements of both graphs. There are no common vertices in g1 and g2, hence there are no vertices in the overlap graph.
Given two graphs a and b, the exclusion operator creates a LogicalGraph that includes the edges and vertices of graph a that do not occur in graph b.
It is implemented by the exclude() function of the LogicalGraph. The exclude function takes a LogicalGraph as its input and outputs a new
LogicalGraph consisting of the elemtents of graph a without the elements of graph b.
Consider the social graph from our quickstart section.
We use the exclude function to retrieve all elements from graph n1 that do not occur in n2.
LogicalGraph exlusion = n1.exclude(n2);The resulting graph looks as follows:

Given two graphs, the equality operator determines whether they are equal.
The operator is implemented by the LogicalGraph. The equal operator takes another Logical Graph as its input and outputs a DataSet<Boolean> that contains a single boolean value.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| equalsByData | Compares the vertices, edges and the label, properties of the LogicalGraphs for equality. |
| equalsByElementData | Compares the vertices and edges of the LogicalGraphs for equality. |
| equalsByElementIds | Compares the vertices and edges of the LogicalGraphs for equality by using their internal ID. Therefore, 2 graphs may have vertices and edges with the same properties without being equal. |
tbd.
