|
1 | | -# metro-fare-calculator |
| 1 | +# Python Anywhere CI/CD pipeline POC |
2 | 2 |
|
3 | | -Metro Fare Calculator is a simple web application designed to help users calculate the fare for their metro rides. With this application, users can easily determine the cost of their metro ride based on their starting and ending stations. |
4 | 3 |
|
5 | 4 |
|
6 | | - |
7 | | -The application is built using the Django framework and is designed to be responsive and easy to use. Users simply select their starting station and ending station from a dropdown menu, and the application calculates the fare based on the distance between the two stations. |
8 | | - |
9 | 5 | I have created CI/CD pipelines to automatically deploy code updates on Github repository to pythonanywhere web application. |
10 | 6 |
|
11 | 7 | Automating Code Deployment from GitHub to PythonAnywhere |
@@ -153,54 +149,7 @@ Conclusion |
153 | 149 |
|
154 | 150 | This guide helps automate deployment from GitHub to PythonAnywhere using API calls. Once set up, every push to GitHub updates the PythonAnywhere project automatically and reloads the web app. 🚀 |
155 | 151 |
|
156 | | - |
157 | | - |
158 | | -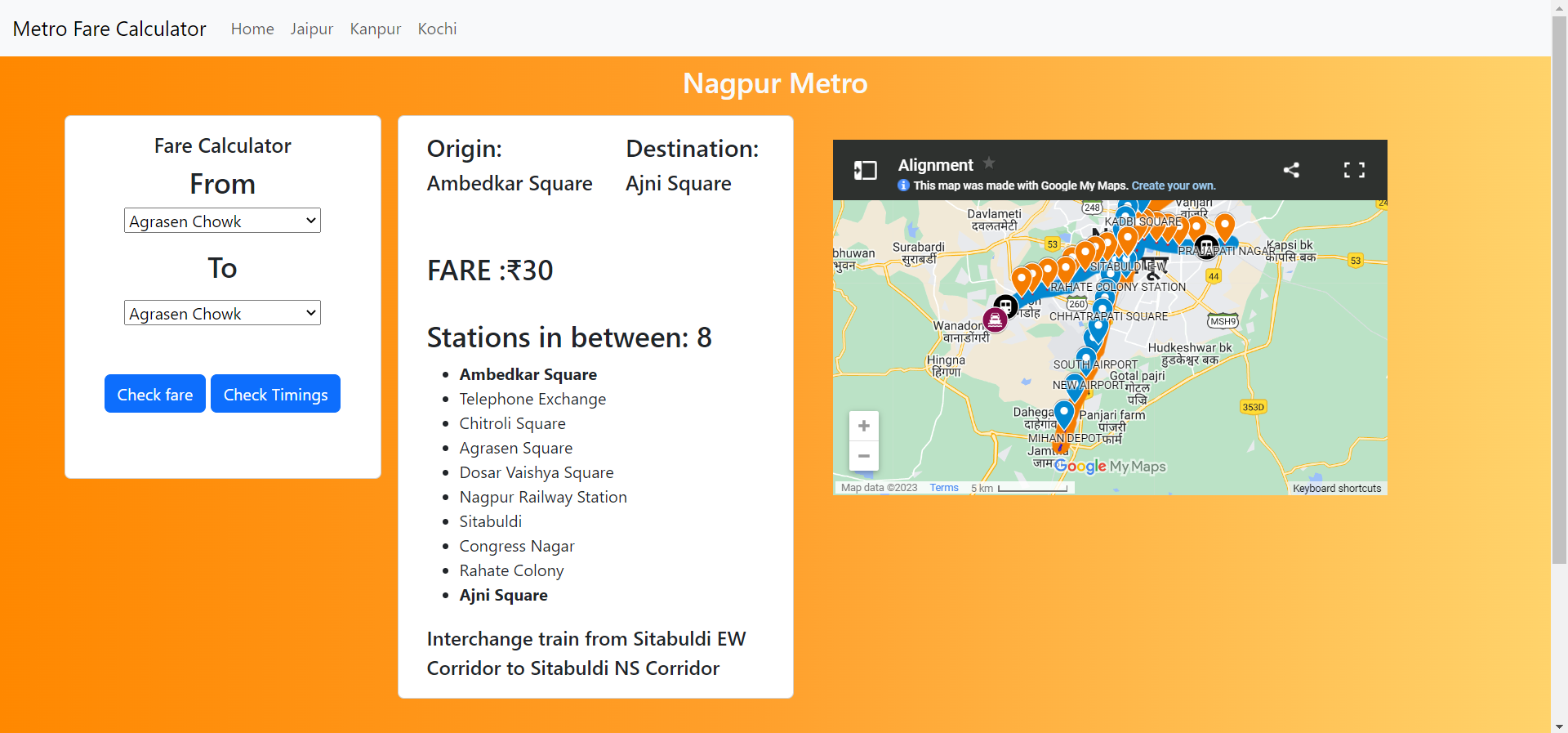 |
159 | | - |
160 | | - |
161 | | -If you are looking for a reliable and user-friendly metro fare calculator, this project is an excellent choice. It is free and open-source, so feel free to fork the repository and make contributions to improve the application further. |
162 | | - |
163 | | -1. Install Python: If you haven't already, download and install the latest version of Python for your operating system from the official website: https://www.python.org/downloads/ |
164 | | - |
165 | | -2. Install Git: Download and install Git for your operating system from the official website: https://git-scm.com/downloads |
166 | | - |
167 | | -3. Clone the project: Open your terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory where you want to store the project. Then, run the following command to clone the project: |
168 | | - |
169 | | -git clone https://github.com/username/project.git |
170 | | - |
171 | | -4. Replace the username with the username of the person who created the project and the project with the name of the project. |
172 | | - |
173 | | -5. Install virtualenv: Virtualenv is a tool that allows you to create isolated Python environments for each project, so you don't have to worry about dependencies conflicting with each other. To install virtualenv, run the following command: |
174 | | - |
175 | | -pip install virtualenv |
176 | | - |
177 | | -6. Create a virtual environment: Navigate to the project directory and create a new virtual environment by running the following command: |
178 | | - |
179 | | -virtualenv env |
180 | | - |
181 | | -7. Activate the virtual environment: Activate the virtual environment by running the following command: |
182 | | - |
183 | | -For Windows: |
184 | | - |
185 | | -env\Scripts\activate |
186 | | - |
187 | | -For macOS or Linux: |
188 | | - |
189 | | -source env/bin/activate |
190 | | - |
191 | | -8. Install dependencies: Once the virtual environment is activated, install the required dependencies by running the following command: |
192 | | - |
193 | | -pip install -r requirements.txt |
194 | | - |
195 | | -9. Set up the database: Before you can run the Django project, you need to set up the database. Run the following commands in order: |
196 | | - |
197 | | -python manage.py makemigrations |
198 | | - |
199 | | -python manage.py migrate |
200 | | - |
201 | | -10.Run the server: Finally, run the Django server by running the following command: |
202 | 152 |
|
203 | | -python manage.py runserver |
204 | 153 |
|
205 | 154 | This should start the server on http://127.0.0.1:8000/ or http://localhost:8000/. |
206 | 155 |
|
|
0 commit comments